Cold-cache Sequential I/O Benchmark
CCSIO Benchmark measures maximum sequential read/write
speed that is achievable for a given volume and the file
stack below it.
In plain terms, it measures how fast one can possibly read/write very large files from/to specified location.
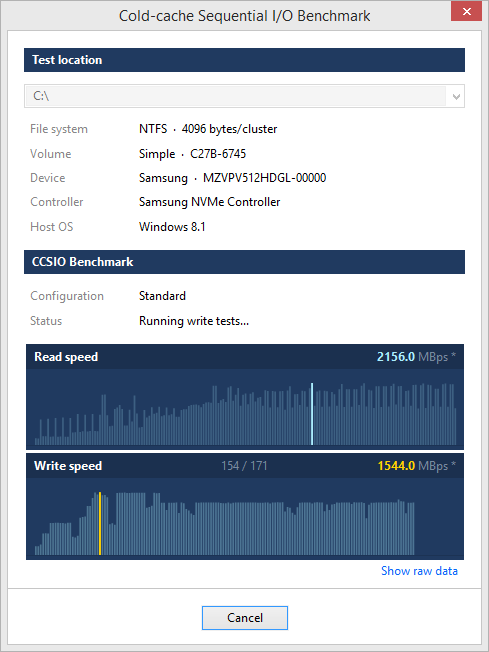 Benchmark can be used to assess performance of file systems
residing on local drives, remote network shares as well as
virtual/pseudo devices such as RAM disks and encrypted file
containers.
Benchmark can be used to assess performance of file systems
residing on local drives, remote network shares as well as
virtual/pseudo devices such as RAM disks and encrypted file
containers.
In plain terms, it measures how fast one can possibly read/write very large files from/to specified location.
 Benchmark can be used to assess performance of file systems
residing on local drives, remote network shares as well as
virtual/pseudo devices such as RAM disks and encrypted file
containers.
Benchmark can be used to assess performance of file systems
residing on local drives, remote network shares as well as
virtual/pseudo devices such as RAM disks and encrypted file
containers.
Download CCSIO Benchmark
| Requires | Windows Vista or newer |
| File size | 238 KB |
| Version | 1.5.0 |
| Released | June 26, 2019 |
What it does
Reading/writing files involves passing memory buffers
(blocks) to the operating system and asking it to either
fill it with on-disk data or dump buffer contents into
the file.
There are three principal variables involved in the process:
Have a look at Fundamentals of Fast Bulk IO for all the technical details. As it turns out a winning combination varies greatly with the type of the physical device, its connection to the host as well as the composition of the file stack. What works well for SSD drives often doesn't work for HDD or virtual disks and vice versa.
Here's an example. Values in bold are the maximum read speeds for respective devices:
There are three principal variables involved in the process:
- IO buffer count
- IO buffer size
- IO caching mode
Have a look at Fundamentals of Fast Bulk IO for all the technical details. As it turns out a winning combination varies greatly with the type of the physical device, its connection to the host as well as the composition of the file stack. What works well for SSD drives often doesn't work for HDD or virtual disks and vice versa.
Here's an example. Values in bold are the maximum read speeds for respective devices:
| 8 x 512 KB | 16 x 2 MB | |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung MZVPV512, NVMe | 2158.0 MBps | 1974.1 MBps |
| TrueCrypt volume on SSD | 317.5 MBps | 338.4 MBps |
Benchmark details
By default the benchmark is set up as follows:
A combination of these three parameters is a test run, so
a single benchmark comprises 180 read tests and 120 write tests - 12 sizes
x 5 counts x (2 or 3) modes - to the grand total of 300 tests per benchmark.
There's also a 64MB memory cap on all tests. Tests with total buffer space exceeding this limit are skipped. This brings down the number of tests to 285 and about 5 minutes of total run time.
When testing remote volumes local file buffering is disabled.
Default file size is 2GB, but a smaller file may be used with volumes with low write speeds.
SSD drives and remote volumes - test file is created by filling it with random data.
All other cases - test file is created by setting its valid data length to the desired size. This is a very fast way to create a large file, but it causes some SSD to show faster read rates, because they keep track of which parts of a file were actually written to.
| Buffer sizes |
8K, 16K, 32K, 64K, 128K, 256K, 512K, 1M, 2M, 4M, 8M, 16M |
|
| Buffer counts | 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 | |
| IO modes |
Unbuffered Unbuffered sequential Buffered sequential |
(read / write) (read / write) (read only) |
Test limits
Duration of each test is 1 second, which is usually sufficient to get an accurate speed estimate on an idle machine. This is a soft limit, meaning that a test may actually take a bit longer to complete.There's also a 64MB memory cap on all tests. Tests with total buffer space exceeding this limit are skipped. This brings down the number of tests to 285 and about 5 minutes of total run time.
Cache control
When testing local volumes Windows file cache is flushed before every test by clearing the system Standby List.When testing remote volumes local file buffering is disabled.
Test file
All tests are run against a large test file that is created at the root of test location before the first test and removed after all tests are completed.Default file size is 2GB, but a smaller file may be used with volumes with low write speeds.
SSD drives and remote volumes - test file is created by filling it with random data.
All other cases - test file is created by setting its valid data length to the desired size. This is a very fast way to create a large file, but it causes some SSD to show faster read rates, because they keep track of which parts of a file were actually written to.